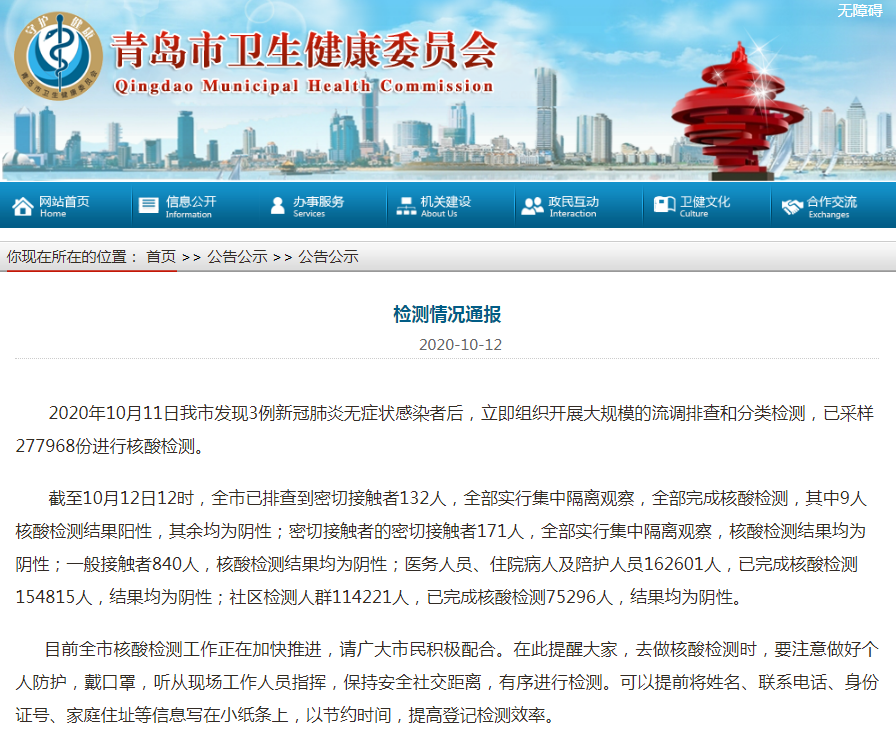
Javaдёӯзҡ„HashMapдёӯзҡ„transient Entry[] table;иҰҒзү№ең°дёҚеәҸеҲ—еҢ–
жҗңдәҶдёҖеңҲпјҢеӨ§жҰӮж•ҙзҗҶиҰҒзӮ№еҰӮдёӢпјҡ
еүҚжҸҗзҹҘиҜҶпјҡ
HashMap жҳҜ дёҖз§Қ Map пјҢдҪҝз”Ё HashCode иҝӣиЎҢзҙўеј•зӯүзӣёе…іж“ҚдҪңпјҢжүҖд»ҘеҸ« HashMapHashCode жҳҜдёҖдёӘ native ж–№жі• пјҢиҜҰи§Ғ java.lang.Object#hashcode()дёҚеҗҢзҡ„ JVM еҜ№ native ж–№жі• жңүдёҚеҗҢзҡ„е®һзҺ°гҖӮеӣ жӯӨпјҢеҪ“дёҖдёӘ HashMap еәҸеҲ—еҢ–еҗҺпјҢиў«еҸҰеӨ–дёҖдёӘ(дёҚеҗҢзҡ„) JVM иҝӣиЎҢеҸҚеәҸеҲ—еҢ–ж—¶пјҡ
з”ұдәҺдёҚеҗҢзҡ„JVM зҡ„ HashCode зҡ„зӯ–з•ҘжңүжүҖдёҚеҗҢпјҢдҪҝз”ЁеҺҹжқҘ JVM дёҠи®Ўз®—зҡ„ HashCode еҖјеңЁеҸҰеӨ–дёҖдёӘ JVM дёҠи®Ўз®—дјҡеј•иө·й”ҷиҜҜгҖӮ
жүҖд»ҘпјҢеҰӮжһңиҰҒеәҸеҲ—еҢ–дёҖдёӘ HashMap пјҢйңҖиҰҒеү”йҷӨ hashcode зҡ„еҪұе“ҚпјҢжүҖд»ҘеұһжҖ§ж ҮиҜҶжҲҗдәҶ transient зұ»еһӢгҖӮ
дёәдәҶе®һзҺ°еәҸеҲ—еҢ–пјҢеҶ…йғЁиҮӘе®ҡд№үдәҶеәҸеҲ—еҢ–зҡ„зӣёе…ізӯ–з•ҘеҰӮдёӢпјҡ(HashMap.java)private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException { int buckets = capacity(); // Write out the threshold, loadfactor, and any hidden stuff s.defaultWriteObject(); s.writeInt(buckets); s.writeInt(size); internalWriteEntries(s); }жҠҠ bucketsгҖҒsize гҖҒthreshold зӯүеұһжҖ§иҝӣиЎҢзӣҙжҺҘзҡ„еәҸеҲ—еҢ–гҖӮ
еҜ№дәҺ HashMap еҶ…зҡ„ EntrySet зҡ„еәҸеҲ—еҢ–ж–№жі•еҶҷеңЁ internalWriteEntries ж–№жі•йҮҢпјҡ(HashMap.java)// Called only from writeObject, to ensure compatible ordering. void internalWriteEntries(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException { Node\u0026lt;K,V\u0026gt; tab; if (size \u0026gt; 0 \u0026amp;\u0026amp; (tab = table) != null) { for (int i = 0; i \u0026lt; tab.length; ++i) { for (Node\u0026lt;K,V\u0026gt; e = tab; e != null; e = e.next) { s.writeObject(e.key); s.writeObject(e.value); } } } }еҸҜд»ҘзңӢеҲ°жҳҜйҖҡиҝҮ for еҫӘзҺҜйҒҚеҺҶ Node иҝӣиЎҢзҡ„еәҸеҲ—еҢ–ж“ҚдҪңпјҢжҠҠж ёеҝғж•°жҚ®иҝӣиЎҢзҡ„ writeObject ж“ҚдҪңгҖӮ
в– зҪ‘еҸӢ
гҖҗJavaдёӯзҡ„HashMapдёӯзҡ„transient Entry[] table;иҰҒзү№ең°дёҚеәҸеҲ—еҢ–гҖ‘ еҺ»зңӢзңӢеәҸеҲ—еҢ–зҡ„жқЎд»¶д»ҘеҸҠдҪңз”Ё
жҺЁиҚҗйҳ…иҜ»
- й„Ӯжё©е…ӢеҶ¬еӯЈй©¬иөӣ-30в„ғжһҒеҜ’ејҖиөӣпјҡеҜ’еҶ¬дёӯзҡ„зҒ«зғӯжҙҫеҜ№
- еӨ§йӣӘ@еӨ§йӣӘи…ҢиӮү йҖӮеҪ“иҝӣиЎҘ д»Ҡж—ҘеӨ§йӣӘ
- |з”өе•ҶдәӢдёҡдёӯзҡ„вҖңй—Әе…үе°‘е№ҙвҖқ
- dartиҝҷзј–зЁӢиҜӯиЁҖзҺ°еңЁеҸ‘еұ•жҖҺд№Ҳж ·дәҶпјҢиҜӯжі•дёҺJavaпјҢc#еҫҲзӣёдјјпјҢз”ҡиҮіжӣҙз®ҖжҙҒ
- hadoopдёӯзҡ„mapreduceй“ҫжҺҘпјҲmapreduce chainingпјүжҖҺж ·йҒҝе…Қдёӯй—ҙж–Ү件зҡ„дә§з”ҹ
- з»Ҹи§ӮжұҪиҪҰ|ж—Ҙзі»иҪҰдјҒдёӯзҡ„вҖңејӮзұ»вҖқпјҹдёңйЈҺж—Ҙдә§е°ҶеҜје…Ҙe-POWERжҠҖжңҜеӨ§е№ІеўһзЁӢејҸж··еҠЁ | з»Ҹи§ӮжұҪиҪҰ
- дёӯе№ҙ|иҝҷдәӣдёңиҘҝпјҢжҜ”дҪ жғіиұЎдёӯзҡ„иҝҳиҰҒеӨ§еҫ—еӨҡпјҒ
- Javaе·ҘзЁӢеёҲе’ҢC++е·ҘзЁӢеёҲеңЁе·ҘдҪңдёҠжңүе•ҘеҢәеҲ«е“ӘдёӘжӣҙйҖӮеҗҲиҮӘиә«еҸ‘еұ•
- иҜ·й—®жқЁжҜ…еҫ®еҚҡдёӯзҡ„иҝҷдёӨдәәжҳҜи°Ғ
- жҹҗдәӣе…¬еҸёжӢӣиҒҳиҰҒжұӮдёӯзҡ„зІҫйҖҡmysqlжҳҜе•ҘзЁӢеәҰ