йқўиҜ•е®ҳпјҡиҒҠиҒҠ etcd дёӯзҡ„ Raft еҗ§( еӣӣ )
 ж–Үз« жҸ’еӣҫ
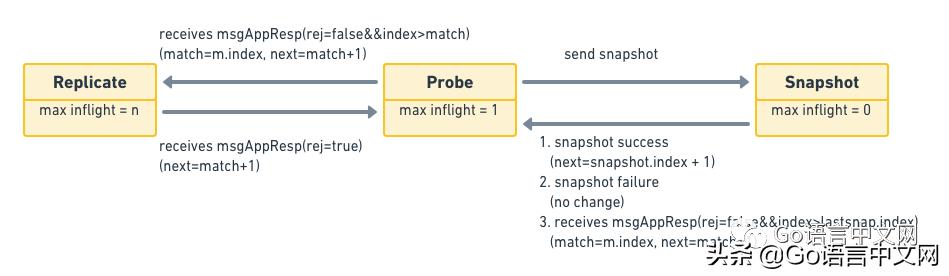
ж–Үз« жҸ’еӣҫProgress State Machine
raft.goеүҚйқўй“әи®ҫдәҶдёҖеӨ§е ҶжҰӮеҝө пјҢ зҺ°еңЁз»ҲдәҺиҪ®еҲ°е®һзҺ°йҖ»иҫ‘дәҶ гҖӮ д»ҺеҗҚеӯ—д№ҹеҸҜд»ҘзңӢеҮә пјҢ raft еҚҸи®®зҡ„е…·дҪ“е®һзҺ°е°ұеңЁиҝҷдёӘж–Ү件йҮҢ гҖӮ иҝҷе…¶дёӯ пјҢ еӨ§йғЁеҲҶзҡ„йҖ»иҫ‘жҳҜз”ұStepеҮҪж•°й©ұеҠЁзҡ„ гҖӮ
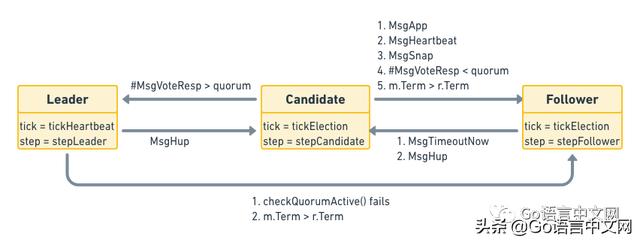
// #L752func (r *raft) Step(m pb.Message) error {//...switch m.Type {case pb.MsgHup://...case pb.MsgVote, pb.MsgPreVote://...default:r.step(r, m)}}Stepзҡ„дё»иҰҒдҪңз”ЁжҳҜеӨ„зҗҶдёҚеҗҢзҡ„ж¶ҲжҒҜ[17] пјҢ жүҖд»Ҙд»ҘеҗҺеҪ“жҲ‘们жғізҹҘйҒ“ raft еҜ№жҹҗз§Қж¶ҲжҒҜзҡ„еӨ„зҗҶйҖ»иҫ‘ж—¶ пјҢ еҲ°иҝҷйҮҢжүҫе°ұеҜ№дәҶ гҖӮ еңЁеҮҪж•°зҡ„жңҖеҗҺ пјҢ жңүдёӘdefaultиҜӯеҸҘ пјҢ еҚіжүҖжңүдёҠйқўдёҚиғҪеӨ„зҗҶзҡ„ж¶ҲжҒҜйғҪиҗҪе…ҘиҝҷйҮҢ пјҢ з”ұдёҖдёӘе°ҸеҶҷзҡ„stepеҮҪж•°еӨ„зҗҶ пјҢ иҝҷдёӘи®ҫи®Ўзҡ„еҺҹеӣ жҳҜд»Җд№Ҳе‘ўпјҹе…¶е®һжҳҜеӣ дёәиҝҷйҮҢзҡ„ raft д№ҹиў«е®һзҺ°дёәдёҖдёӘзҠ¶жҖҒжңә пјҢ е®ғзҡ„stepеұһжҖ§жҳҜдёҖдёӘеҮҪж•°жҢҮй’Ҳ пјҢ ж №жҚ®еҪ“еүҚиҠӮзӮ№зҡ„дёҚеҗҢи§’иүІ пјҢ жҢҮеҗ‘дёҚеҗҢзҡ„ж¶ҲжҒҜеӨ„зҗҶеҮҪж•°пјҡstepLeader[18]/stepFollower[19]/stepCandidate[20] гҖӮ дёҺе®ғзұ»дјјзҡ„иҝҳжңүдёҖдёӘtickеҮҪж•°жҢҮй’Ҳ пјҢ ж №жҚ®и§’иүІзҡ„дёҚеҗҢ пјҢ д№ҹдјҡеңЁtickHeartbeat[21]е’ҢtickElection[22]д№Ӣй—ҙжқҘеӣһеҲҮжҚў пјҢ еҲҶеҲ«з”ЁжқҘи§ҰеҸ‘е®ҡж—¶еҝғи·іе’ҢйҖүдёҫжЈҖжөӢ гҖӮ иҝҷйҮҢзҡ„еҮҪж•°жҢҮй’Ҳж„ҹи§үеғҸе®һзҺ°дәҶOOPйҮҢзҡ„еӨҡжҖҒ гҖӮ
 ж–Үз« жҸ’еӣҫ
ж–Үз« жҸ’еӣҫRaft State Machine
node.gonodeзҡ„дё»иҰҒдҪңз”ЁжҳҜеә”з”ЁеұӮпјҲetcdserverпјүе’Ңе…ұиҜҶжЁЎеқ—пјҲraftпјүзҡ„иЎ”жҺҘ гҖӮ е°Ҷеә”з”ЁеұӮзҡ„ж¶ҲжҒҜдј йҖ’з»ҷеә•еұӮе…ұиҜҶжЁЎеқ— пјҢ 并е°Ҷеә•еұӮе…ұиҜҶжЁЎеқ—е…ұиҜҶеҗҺзҡ„з»“жһңеҸҚйҰҲз»ҷеә”з”ЁеұӮ гҖӮ жүҖд»Ҙе®ғзҡ„еҲқе§ӢеҢ–еҮҪж•°[23]еҲӣе»әдәҶеҫҲеӨҡз”ЁжқҘйҖҡдҝЎзҡ„channel пјҢ 然еҗҺе°ұеңЁеҸҰдёҖдёӘgoroutineйҮҢйқўејҖе§ӢдәҶдәӢ件еҫӘзҺҜ пјҢ дёҚеҒңзҡ„еңЁеҗ„з§ҚchannelдёӯеҖ’и…ҫж•°жҚ®пјҲиІҢдјјиҝҷз§Қз”ұfor-select-channelз»„жҲҗзҡ„дәӢ件еҫӘзҺҜеңЁ Go йҮҢйқўеҫҲеҸ—ж¬ўиҝҺпјү гҖӮ
// #L286for {select {case m := <-propc:r.Step(m)case m := <-n.recvc:r.Step(m)case cc := <-n.confc:// Add/remove/update node according to cc.Typecase <-n.tickc:r.tick()case readyc <- rd:// Cleaning after result is consumed by applicationcase <-advancec:// Stablize logscase c := <-n.status:// Update statuscase <-n.stop:close(n.done)return}}propcе’ҢrecvcдёӯжӢҝеҲ°зҡ„жҳҜд»ҺдёҠеұӮеә”з”Ёдј иҝӣжқҘзҡ„ж¶ҲжҒҜ пјҢ иҝҷдёӘж¶ҲжҒҜдјҡиў«дәӨз»ҷ raft еұӮзҡ„StepеҮҪж•°еӨ„зҗҶ пјҢ е…·дҪ“еӨ„зҗҶйҖ»иҫ‘жҲ‘дёҠйқўжңүиҝҮд»Ӣз»Қ гҖӮдёӢйқўжқҘи§ЈйҮҠдёӢreadycзҡ„дҪңз”Ё гҖӮ еңЁ etcd зҡ„иҝҷдёӘе®һзҺ°дёӯ пјҢ node并дёҚиҙҹиҙЈж•°жҚ®зҡ„жҢҒд№…еҢ–гҖҒзҪ‘з»ңж¶ҲжҒҜзҡ„йҖҡдҝЎгҖҒд»ҘеҸҠе°Ҷе·Із»ҸжҸҗдәӨзҡ„ log еә”з”ЁеҲ°зҠ¶жҖҒжңәдёӯ пјҢ жүҖд»ҘnodeдҪҝз”ЁreadycиҝҷдёӘchannelеҜ№еӨ–йҖҡзҹҘжңүж•°жҚ®иҰҒеӨ„зҗҶдәҶ пјҢ 并е°ҶиҝҷдәӣйңҖиҰҒеӨ–йғЁеӨ„зҗҶзҡ„ж•°жҚ®жү“еҢ…еҲ°дёҖдёӘReadyз»“жһ„дҪ“дёӯпјҡ
// #L52// Ready encapsulates the entries and messages that are ready to read,// be saved to stable storage, committed or sent to other peers.// All fields in Ready are read-only.type Ready struct {// The current volatile state of a Node.// SoftState will be nil if there is no update.// It is not required to consume or store SoftState.*SoftState// The current state of a Node to be saved to stable storage BEFORE// Messages are sent.// HardState will be equal to empty state if there is no update.pb.HardState// ReadStates can be used for node to serve linearizable read requests locally// when its applied index is greater than the index in ReadState.// Note that the readState will be returned when raft receives msgReadIndex.// The returned is only valid for the request that requested to read.ReadStates []ReadState// Entries specifies entries to be saved to stable storage BEFORE// Messages are sent.Entries []pb.Entry// Snapshot specifies the snapshot to be saved to stable storage.Snapshot pb.Snapshot// CommittedEntries specifies entries to be committed to a// store/state-machine. These have previously been committed to stable// store.CommittedEntries []pb.Entry// Messages specifies outbound messages to be sent AFTER Entries are// committed to stable storage.// If it contains a MsgSnap message, the application MUST report back to raft// when the snapshot has been received or has failed by calling ReportSnapshot.Messages []pb.Message// MustSync indicates whether the HardState and Entries must be synchronously// written to disk or if an asynchronous write is permissible.MustSync bool}
жҺЁиҚҗйҳ…иҜ»
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- иҒҠиҒҠзҪ‘жҳ“дә‘йҹід№җпјҡвҖңеҝғеҠЁжЁЎејҸвҖқ
- еҚҺдёәзӘҒ然宣еёғпјҒи…ҫи®Ҝд№ҹжІЎжңүжғіеҲ°пјҢдёҖеҲҮжқҘеҫ—еҰӮжӯӨеҝ«
- е…ЁзҗғжңҖеҸ—ж¬ўиҝҺзҡ„4йғЁ5GжүӢжңәпјҡйқ йҮҸеҸ–иғңзҡ„е°Ҹзұіз«ҹжҰңдёҠж— еҗҚпјҹ
- JavaеӯҰд№ пјҡJavaеӯҰд№ еҲ°д»Җд№ҲзЁӢеәҰеҸҜд»ҘиҝӣиЎҢйқўиҜ•
- зЁӢеәҸе‘ҳйқўиҜ•йҮ‘е…ё17.05_go_еӯ—жҜҚдёҺж•°еӯ—
- е®үеҚ“жҳҘжӢӣйқўз»ҸпјҡдәҢжң¬жёЈйҷўйқўиҜ•зҪ‘жҳ“иў«жӢ’пјҢжңҖз»ҲиҺ·и…ҫи®ҜйҳҝйҮҢoffer
- дёӯеӣҪжңҖиөҡй’ұзҡ„е…¬еҸёиҜһз”ҹпјҒдёҚжҳҜ移еҠЁпјҢд№ҹдёҚжҳҜйҳҝйҮҢе·ҙе·ҙпјҢйӮЈз¬¬дёҖжҳҜпјҹ
- гҖҢ6гҖҚиҝӣеӨ§еҺӮеҝ…йЎ»жҺҢжҸЎзҡ„йқўиҜ•йўҳ-Hibernate
- й«ҳйҖҡйӘҒйҫҷ888жҸҗеүҚжқҘдәҶпјҒеҚҺдёәвҖңж…ҢвҖқдәҶпјҹдҪҶдёҖеҲҮиҝҳжІЎжңүе®ҡи®ә
- йңҮжғҠпјҒдә¬дёңT4еӨ§дҪ¬йқўиҜ•ж•ҙж•ҙдёүдёӘжңҲпјҢжүҚеҶҷдәҶдёӨд»ҪjavaйқўиҜ•з¬”и®°

















![[дёӨеј№дёҖжҳҹ]е”ҜдёҖеңЁеӨ©з©әй—ӘзғҒзҡ„зүӣйғҺз»ҮеҘі дёӨеј№дёҖжҳҹзғҲеЈ«е’ҢжңҖзҫҺйҷўеЈ«еңЁеӨ©дёҠзӣёдјҡ](https://p0.ssl.qhimgs4.com/t010247be3077dad79a.jpg?size=600x400)

