爱可可AI论文推介(10月13日)( 二 )
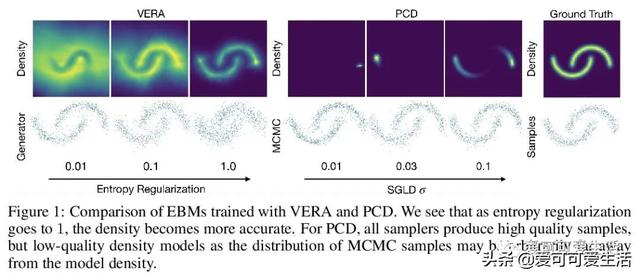 文章插图
文章插图
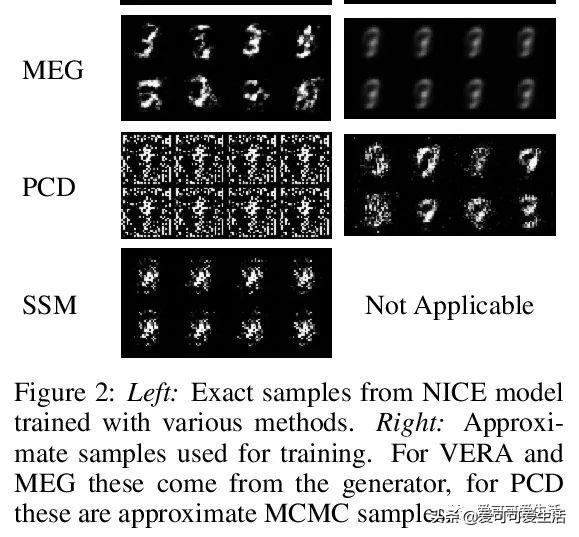 文章插图
文章插图
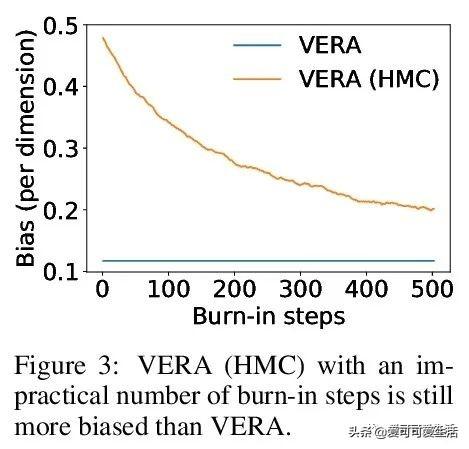 文章插图
文章插图
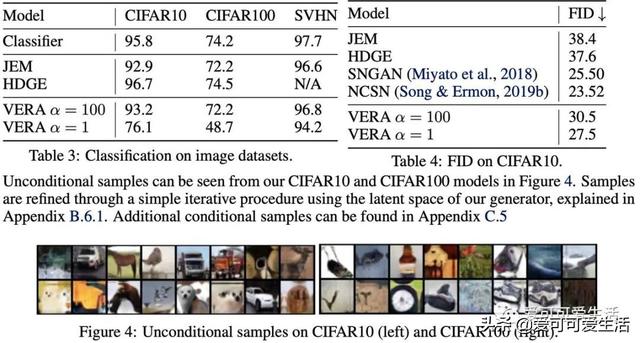 文章插图
文章插图
3、[LG]*Metrics and methods for a systematic comparison of fairness-aware machine learning algorithms
G P. Jones, J M. Hickey, P G. D Stefano, C Dhanjal, L C. Stoddart, V Vasileiou
[Experian DataLabs UK&I and EMEA]
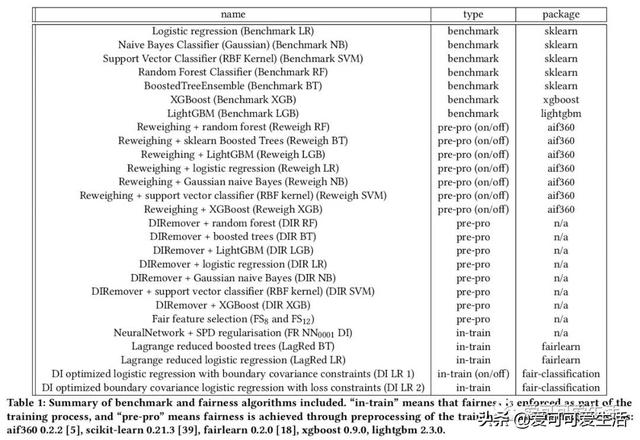
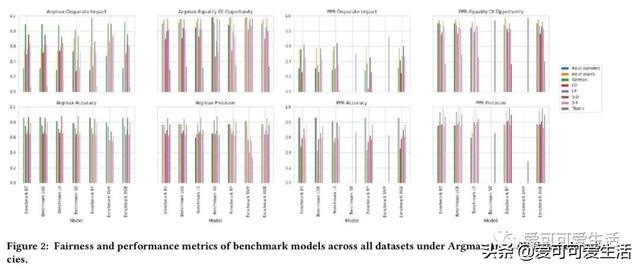
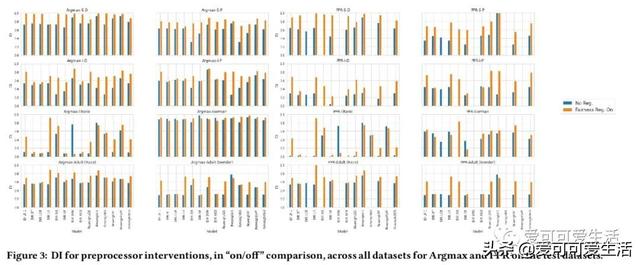
公平感知机器学习算法的系统比较 , 对一些普遍适用于监督分类的公平性算法进行了系统比较 , 评价了28种不同模型 , 包括7种非公平(基准)机器学习算法和由8种公平方法驱动的20种公平感知模型 。 使用3个决策阈值策略、7个数据集、2个公平性指标和3个预测性能指标 , 对公平感知机器学习算法的公平性、预测性能、校准质量和速度进行评价 。
Understanding and removing bias from the decisions made by machine learning models is essential to avoid discrimination against unprivileged groups. Despite recent progress in algorithmic fairness, there is still no clear answer as to which bias-mitigation approaches are most effective. Evaluation strategies are typically use-case specific, rely on data with unclear bias, and employ a fixed policy to convert model outputs to decision outcomes. To address these problems, we performed a systematic comparison of a number of popular fairness algorithms applicable to supervised classification. Our study is the most comprehensive of its kind. It utilizes three real and four synthetic datasets, and two different ways of converting model outputs to decisions. It considers fairness, predictive-performance, calibration quality, and speed of 28 different modelling pipelines, corresponding to both fairness-unaware and fairness-aware algorithms. We found that fairness-unaware algorithms typically fail to produce adequately fair models and that the simplest algorithms are not necessarily the fairest ones. We also found that fairness-aware algorithms can induce fairness without material drops in predictive power. Finally, we found that dataset idiosyncracies (e.g., degree of intrinsic unfairness, nature of correlations) do affect the performance of fairness-aware approaches. Our results allow the practitioner to narrow down the approach(es) they would like to adopt without having to know in advance their fairness requirements.
 文章插图
文章插图
 文章插图
文章插图
 文章插图
文章插图
4、[CL]Automatic Extraction of Rules Governing Morphological Agreement
A Chaudhary, A Anastasopoulos, A Pratapa, D R. Mortensen, Z Sheikh, Y Tsvetkov, G Neubig
[CMU & George Mason University]
从给定语言的原始文本自动提取形态一致性规则 , 发布了55种语言的提取规则 。 该方法先对原始文本进行句法分析 , 预测词性标签、依存句法分析和词法特征 , 在这些分析数据的基础上学习协议预测模型(决策树) 。
推荐阅读
- 谷歌:想发AI论文?请保证写的是正能量
- 谷歌对内部论文进行“敏感问题”审查!讲坏话的不许发
- 2019年度中国高质量国际科技论文数排名世界第二
- 谷歌通过启动敏感话题审查来加强对旗下科学家论文的控制
- Arxiv网络科学论文摘要11篇(2020-10-12)
- 聚焦城市治理新方向,5G+智慧城市推介会在长举行
- 中国移动5G新型智慧城市全国推介会在长沙举行
- 年年都考的数字鸿沟有了新进展?彭波老师的论文给出了解答!
- 打开深度学习黑箱,牛津大学博士小姐姐分享134页毕业论文
- 爱可可AI论文推介(10月9日)













![[励志视频短片]做好事,微笑挂满两腮才是正道!,早安心语:存好心](https://imgcdn.toutiaoyule.com/20200503/20200503054140414532a_t.jpeg)



