MybatisжҳҜеҰӮдҪ•жү§иЎҢдёҖжқЎSQLе‘Ҫд»Өзҡ„
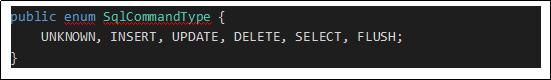
Mybatisдёӯзҡ„Sqlе‘Ҫд»Ө пјҢ еңЁжһҡдёҫзұ»SqlCommandTypeдёӯе®ҡд№үзҡ„ гҖӮ
 ж–Үз« жҸ’еӣҫ
ж–Үз« жҸ’еӣҫ
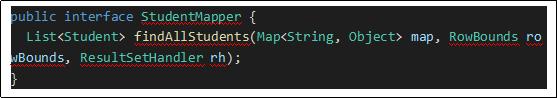
дёӢйқў пјҢ жҲ‘们д»ҘMapperжҺҘеҸЈдёӯзҡ„дёҖдёӘж–№жі•дҪңдёәдҫӢеӯҗ пјҢ зңӢзңӢSqlе‘Ҫд»Өзҡ„жү§иЎҢе®Ңж•ҙжөҒзЁӢ гҖӮ
 ж–Үз« жҸ’еӣҫ
ж–Үз« жҸ’еӣҫ
еҸӮж•°RowBoundsе’ҢResultSetHandlerжҳҜеҸҜйҖүеҸӮж•° пјҢ иЎЁзӨәеҲҶйЎөеҜ№иұЎе’ҢиҮӘе®ҡд№үз»“жһңйӣҶеӨ„зҗҶеҷЁ пјҢ дёҖиҲ¬дёҚйңҖиҰҒ гҖӮ
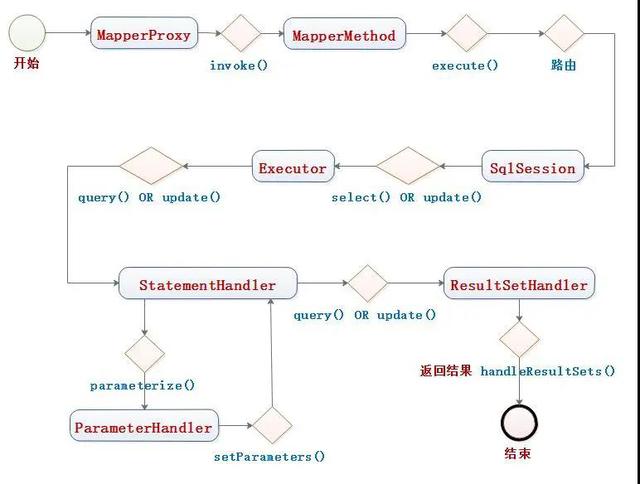
дёҖдёӘе®Ңж•ҙзҡ„Sqlе‘Ҫд»Ө пјҢ е…¶жү§иЎҢзҡ„е®Ңж•ҙжөҒзЁӢеӣҫеҰӮдёӢпјҡ
 ж–Үз« жҸ’еӣҫ
ж–Үз« жҸ’еӣҫ
еҜ№дәҺдёҠйқўзҡ„жөҒзЁӢеӣҫ пјҢ еҰӮжһңзңӢиҝҮеүҚйқўзҡ„ж–Үз« зҡ„иҜқ пјҢ еӨ§йғЁеҲҶеҜ№иұЎжҲ‘们йғҪжҜ”иҫғзҶҹжӮүдәҶ гҖӮ дёҖдёӘеӣҫ пјҢ е°ұе®Ңж•ҙеұ•зӨәдәҶе…¶жү§иЎҢжөҒзЁӢ гҖӮ
MapperProxyзҡ„еҠҹиғҪпјҡ
1. еӣ дёәMapperжҺҘеҸЈдёҚиғҪзӣҙжҺҘе®һдҫӢеҢ– пјҢ MapperProxyзҡ„дҪңз”Ё пјҢ е°ұжҳҜдҪҝз”ЁJDKеҠЁжҖҒд»ЈзҗҶеҠҹиғҪ пјҢ й—ҙжҺҘе®һдҫӢеҢ–Mapperзҡ„proxyеҜ№иұЎ гҖӮ еҸҜеҸӮзңӢзі»еҲ—зҡ„第дәҢзҜҮ гҖӮ
2. зј“еӯҳMapperMethodеҜ№иұЎ гҖӮ
private final Map
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
// жҠ•йһӯж–ӯжөҒ
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
// зј“еӯҳMapperMethod
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
MapperMethodзҡ„еҠҹиғҪпјҡ
1. и§ЈжһҗMapperжҺҘеҸЈзҡ„ж–№жі• пјҢ 并е°ҒиЈ…жҲҗMapperMethodеҜ№иұЎ гҖӮ
2. е°ҶSqlе‘Ҫд»Ө пјҢ жӯЈзЎ®и·Ҝз”ұеҲ°жҒ°еҪ“зҡ„SqlSessionзҡ„ж–№жі•дёҠ гҖӮ
public class MapperMethod {
// дҝқеӯҳдәҶSqlе‘Ҫд»Өзҡ„зұ»еһӢе’Ңй”®id
private final SqlCommand command;
// дҝқеӯҳдәҶMapperжҺҘеҸЈж–№жі•зҡ„и§ЈжһҗдҝЎжҒҜ
private final MethodSignature method;
public MapperMethod(Class mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, method);
}
// ж №жҚ®и§Јжһҗз»“жһң пјҢ и·Ҝз”ұеҲ°жҒ°еҪ“зҡ„SqlSessionж–№жі•дёҠ
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.UPDATE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.DELETE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
жҺЁиҚҗйҳ…иҜ»
- еӨ§дёҖйқһи®Ўз®—жңәдё“дёҡзҡ„еӯҰз”ҹпјҢеҰӮдҪ•еҲ©з”ЁеҜ’еҒҮиҮӘеӯҰCиҜӯиЁҖ
- зәўзұіK40жёІжҹ“еӣҫжӣқе…үпјҡеұ…дёӯжҢ–еӯ”+еҗҺзҪ®еӣӣж‘„пјҢиҝҷеӨ–и§ӮдҪ и§үеҫ—еҰӮдҪ•пјҹ
- еҘӢж–—|иҜҘеҰӮдҪ•зңӢеҫ…жӢјеӨҡеӨҡе‘ҳе·ҘзҢқжӯ»пјҡйј“еҠұеҘӢж–—пјҢд№ҹиҰҒдҝқжҠӨеҘҪеҘӢж–—иҖ…
- иЈ…жңәзӮ№дёҚдә® еҰӮдҪ•з®Җжҳ“жҺ’жҹҘ硬件问йўҳпјҹ
- иҷҫзұійҹід№җе®Јеёғе…іеҒңпјҒжҲ‘зҡ„жӯҢеҚ•еҰӮдҪ•еҜје…ҘQQйҹід№җгҖҒзҪ‘жҳ“дә‘йҹід№җпјҹ
- дәәи„ёиҜҶеҲ«и®ҫеӨҮдё»жқҝеҰӮдҪ•йҖүеһӢ иҪҜзЎ¬ж•ҙеҗҲеӨ§е№…зј©зҹӯејҖеҸ‘ж—¶й—ҙ
- й«ҳйҖҡе…¬еҸёе®Јеёғд»»е‘Ҫе®үи’ҷдёәеҖҷд»»йҰ–еёӯжү§иЎҢе®ҳ
- Mini-LEDдә§е“Ғж•Ҳжһң究з«ҹеҰӮдҪ•пјҹ
- 专家д»Ӣз»ҚеҰӮдҪ•еҲӨж–ӯжҷәиғҪжүӢжңәиў«е…ҘдҫөпјҡиҝҗиЎҢйҖҹеәҰеҸҳж…ўгҖҒз”өжұ ж¶ҲиҖ—иҝҮеҝ«д»ҘеҸҠеҚЎйЎҝ
- жңҖдҫҝе®ңзҡ„йӘҒйҫҷ888жүӢжңәпјҹзәўзұіK40жӣқе…үпјҡиҝҷеӨ–и§ӮеҰӮдҪ•пјҹ













